REDD options hedge carbon price risk in energy sector
The benefits that REDD-based risk-hedging is able to deliver include drastic reduction of deforestation, lower long-term operating risks for energy producers, and lower electricity price for consumers [1] [2].
Note: Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation (REDD) is an effort to create a financial value for the carbon stored in forests. It offers incentives for developing countries to reduce emissions from forested lands and invest in low-carbon paths to sustainable development.
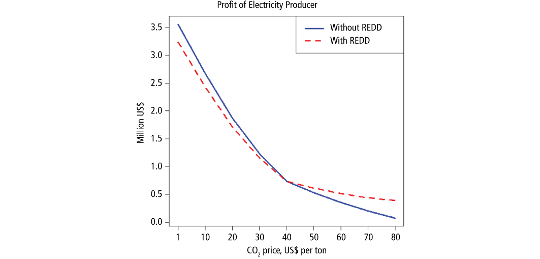
Figure 1. Impact of REDD-based financial instrument on distributions of profits of electricity producer in the model of fairly priced CO2 offsets (click on image to enlarge).
References
[1] Szolgayova J, Golub A, Fuss S (2014). Innovation and risk-averse firms: Options on carbon allowances as a hedging tool. Energy Policy, 70:227-235 (July 2014) (Published online 18 April 2014).
[2] Krasovskii AA, Khabarov N, Obersteiner M (2014). Impacts of the fairly priced REDD-based CO2 offset options on the electricity producers and consumers. Economy of Region, 3(2014):273-288.
Collaborators
Mercator Research Institute on Global Commons and Climate Change, Germany
American University Washington D.C., USA
Research program